As the solar panel cleaning industry continues to develop apace, more and more new entrants are coming into the marketspace. This article is a Glossary of Terms that solar panel cleaners use. Standardisation of terms is important in creating understandable language for our industry. Understanding the language of solar is important if you intend to undergo solar panel cleaning training.
Please note that despite standardisation of terms, certain words and terms are interchangeable. Where they do interchange, the language is still universally understood. One example of this is ‘solar module’ and ‘solar panel’.
Please feel free to submit suggestions to us and help us grow this glossary!
A
AC – Alternating Current, the standard form of current found on a national grid. This current is found post-inverter on solar arrays.
Amp Hour (aH) – Measures a battery’s total capacity. The higher the number, the larger the battery”s capacity.
Amps – Measures the strength of an electrical current.
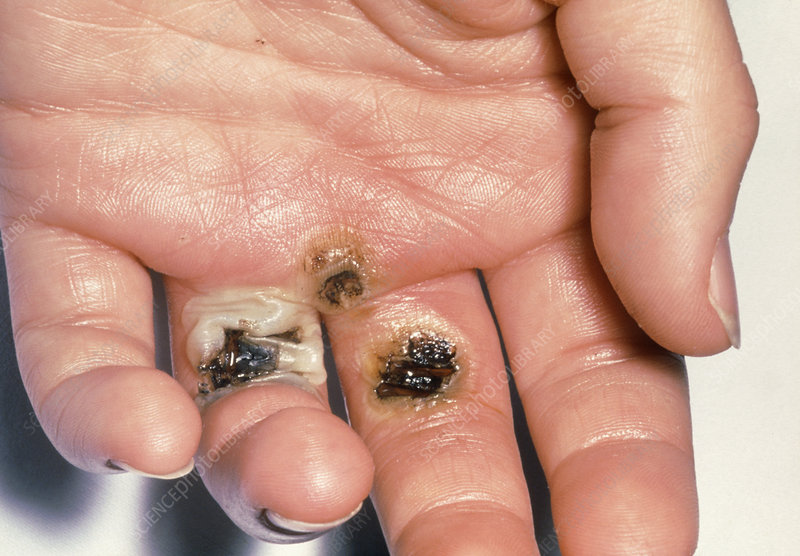
Arcing – Arcing is an electrical discharge that occurs when electrons flow from one source to another, usually metal. For solar panel cleaners, arcing can occur from a damaged part of a solar array to a ring worn on a finger or necklace. Below is an example of a low voltage DC arc on a hand.
B
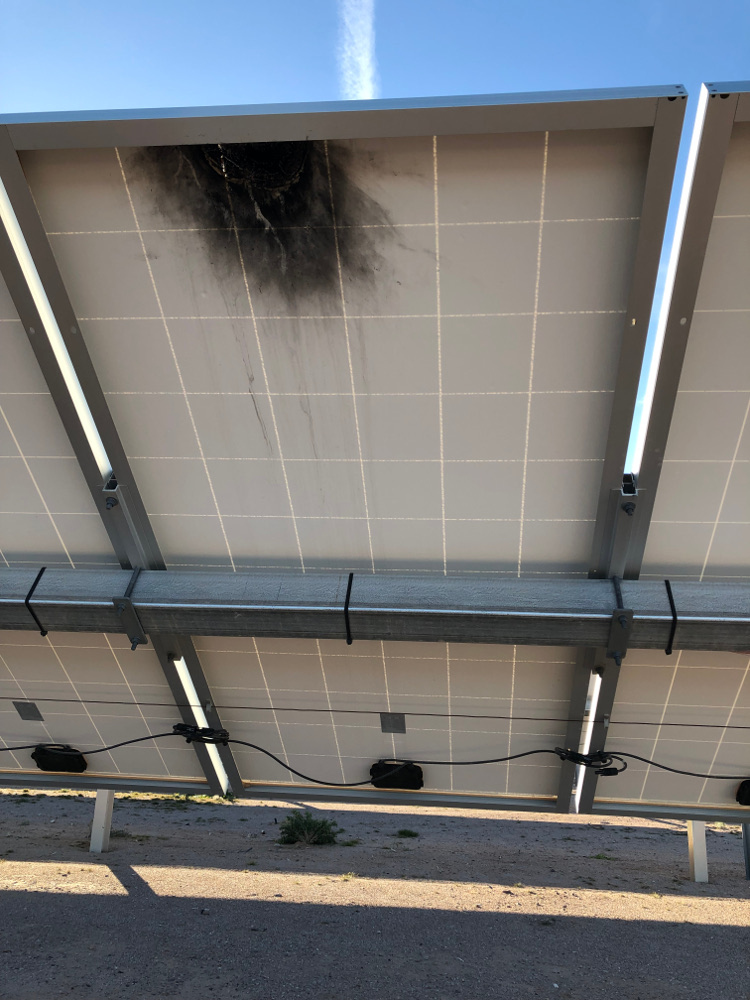
Backsheet – Usually made of a polymer or a combination of polymers, is used to cover the back of solar PV modules. The main function of this layer is to provide electrical isolation of internal circuitry with the external environment. Below is an example of a damaged backsheet.

Birdproofing – The process of fitting a protective barrier, usually mesh, around the perimeter of a solar array to stop birds, rodents and other pests from accessing the underneath of the array.
Browning – This process occurs when moisture enters into a solar panel and overheats or otherwise damages a part of a solar cell or panel. If a solar panel has any browning under the glass anywhere, it should not be cleaned as there is an increased risk of electrocution.

Burnt Cell – A permanently damaged cell within a solar panel that has likely been caused by water ingress or hotspotting. Sometimes evidenced by browning or shown up when the panel is thermal imaged.
Busbar – A metal strip on the front of a solar cell responsible for carrying the electricity out of the cell
Bypass Diode – These are placed in some solar panels at manufacture stage. If the solar panel is partially shaded, bypass diodes prevent the shadowed cells from draining the cells still in the sunlight.
C
C&I – Abbreviation for ‘Commercial & Industrial’, commonly referring to roofmounted solar arrays.
Cell – A solar cell is part of a solar panel. Solar panels are commonly made up of either 60 or 72 cells.
Chemical – A liquid agent that assists with the breakdown of detritus and subsequent cleaning of solar panels. Any chemicals used for cleaning solar panels should have approval of the solar panel manufacturer.
Combiner Box – Combines the output of numerous strings of PV modules for connection to the inverter. Can be found on ground, roof and floating solar arrays.

Crystalline – A type of silicon that is used in solar panels. Most commonly this is either mono-crystalline or poly-crystalline. Crystalline panels tend to be framed and glass-fronted.
Current – Current is measured in Amps
Current – The rate at which electricity flows through a circuit to transfer energy. This can be compared to flow rate in a water pipe, an analogy familiar to most solar panel cleaners.
D
DC – Direct Current is the type of power produced by solar panels and by storage batteries.
DC Cable – A specialized wire designed to transmit the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels to the solar inverter.
DC Connector – Also called the MC4 connector. The DC connector supplies direct current from one solar panel to another. This DC power eventually is connected to the inverter.

Degradation – The process of a solar panel losing power as it ages. The generally accepted and recognized degradation rate is 0.5% annually.
De-ionizing (DI) Resin – A small bead-like substance that catalyzes the ion exchange that rids the water of every non-essential charged ion, creating highly purified water applicable for medical, bio, laboratory use and of course, solar panel cleaning. Also called ‘Ion exchange resin’.
De-ionizer (DI) Tank – A vessel that holds de-ionising or ion exchange resin. The resin removes ionic contaminants that are harmful to many industrial and commercial processes.
De-ionized (DI) Water – Purified water that has had almost all its mineral ions removed, such as cations like sodium, calcium, iron, and copper, and anions like chloride and sulfate.
Delamination – The detachment, even if partially, of the EVA encapsulant from the glass or the backsheet.
Detritus – Waste or debris of any kind that is found anywhere on a solar array.
Dual-Axis Tracker – These solar arrays work on two axes, not only following the sun from east to west, but also from north to south. This allows the solar array to adjust to the ever-changing angle of the sun from season to season.
E
Efficiency – The ratio of sunlight hitting the solar cell to the electrical power it produces. Current solar panel efficiency is around 22% – 24%.
Electroluminescence (EL) Testing – A non-invasive method used to identify microcracks on site and help in proving the root cause – necessary for warranty disputes.
Energy – The product of power and time, measured in Watt-Hours. E.g. 1000 Watt Hours = 1 Kilowatt Hour (kWh)
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) – A material that has good radiation transmission and low degradability to sunlight. This is a thermoplastic polymer, which is used in solar modules as an encapsulating agent since, by applying heat to the assembly, it forms a sealing and insulating film around the solar cells. EVA can discolour, causing the white backsheet of solar panels to look yellow or light brown.

F
Floating Array – A solar array that is mounted on either a still or tidal body of water.
G
Gigawatt – 1,000 Megawatts
Groundmount – A solar array of any size that is mounted on the ground.
H
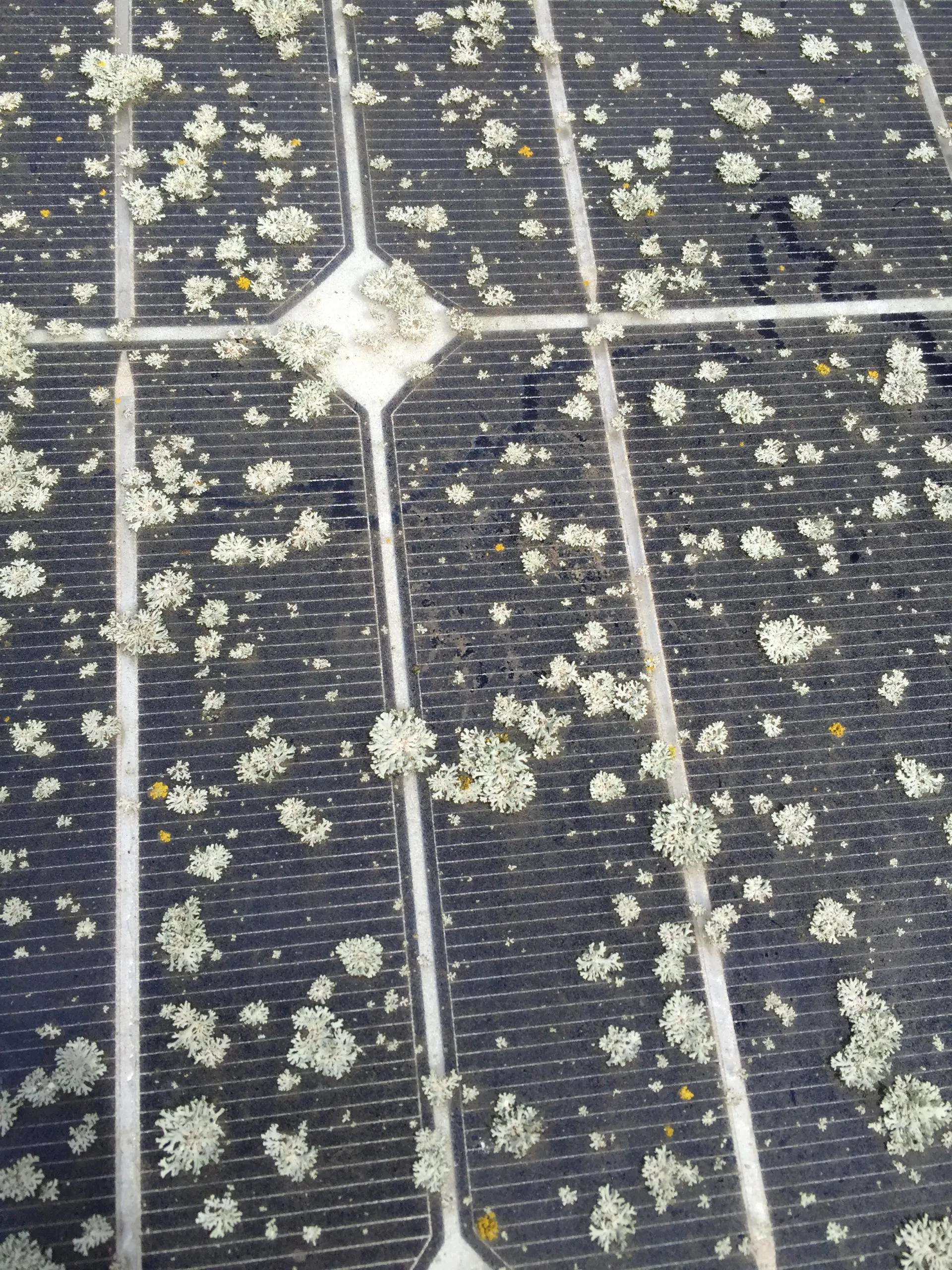
Hard Shading – A shadow cast onto a solar panel that does not move, such as a bird dropping, piece of lichen or other piece of debris.
Hotspot – An overheating part of a solar panel or cell, due to hard or soft shading.
I
Irradiance – The amount of light striking a given surface. In our case, the surface is a solar panel.
Inverter – An electronic device tht converts low voltage DC to high voltage AC power. In solar arrays, inverters take either the 12, 24 or 48 volts DC and convert it to 115 or 230 volts AC, conventional household power.
J
Junction Box – The junction box is a connector between the solar array and the charging control device, it is an important part of the solar panel and is usually located on the rear of the panel.
K
Kilowatt () – 1,000 watts
L
Lichen – Lichen is a stable, symbiotic association between a fungus and algae and/or cyanobacteria.
M
MC4 Connector – Interchangeable term for DC connector. See above.
Megawatt (MW) – 1,000 Kilowatts
Microcrack – Damage created in the silicon wafers inside a solar panel that is most often unseen. This may occur during manufacture, installation or at other times when a solar panel is trodden or walked on. Anyone caught walking on solar panels should be shot at dawn.
Moisture/Water Ingress – Moisture ingress in PV modules is the core of most degradation mechanisms that lead to PV module power degradation. Moisture in EVA encapsulant can lead to metal grids corrosion, delamination and discolouration of encapsulants, potential induced degradation, optical and adhesion losses.
O
Ohm – A measurement of resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of one volt (V) is applied to those points and a current of one ampere (A) is produced.
P
Parts Per Million (P.P.M) – A measure of water quality by a TDS meter in parts per million.
Personal Protective Equipment (P.P.E.) – Equipment worn to minimize exposure to hazards that cause serious workplace injuries and illnesses. These injuries and illnesses may result from contact with chemical, radiological, physical, electrical, mechanical, or other workplace hazards.
Photovoltaic – Photovoltaic (PV) technology converts sunlight into electricity. Commonly referred to as ‘solar’.
Pitch – The angle of a roof or roof mounted solar array.
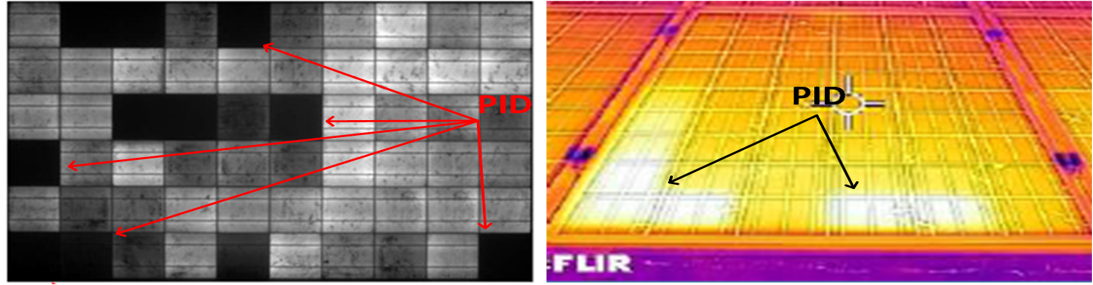
Potential Induced Degradation (PID) – An effect that affects the potential of the modules with respect to the ground and that affects the power of the module by reducing it consistently over time. Often referred to as the ‘cancer of solar panels’.
Power – Measured in Watts (W), is the system voltage multiplied by the system current.
Pressure Washer – An electrical or fuel-driven piece of cleaning equipment that is NOT suitable for solar panel cleaning under any circumstances. Anyone caught using a pressure washer to clean solar panels should be shot at dawn.
PV Array – A group of PV modules (also called panels) arranged to produce the voltage and power desired.
PV Cell – PV cells sit inside and make up a solar module. They are individual PV devices. The most common PV modules are made up of 33 to 36 silicon cells each making 1/2 volt.
PV Module – An assembly of PV cells framed into a weatherproof unit, commonly called a ‘solar panel’.
R
RISO Error – An error message shown by an inverter to show it has detected a ground fault in the PV array or that the PV module’s insulation resistance (R-Iso) is too low. WARNING! Danger to life due to electric shock. In the event of a ground fault, high voltages may be present.
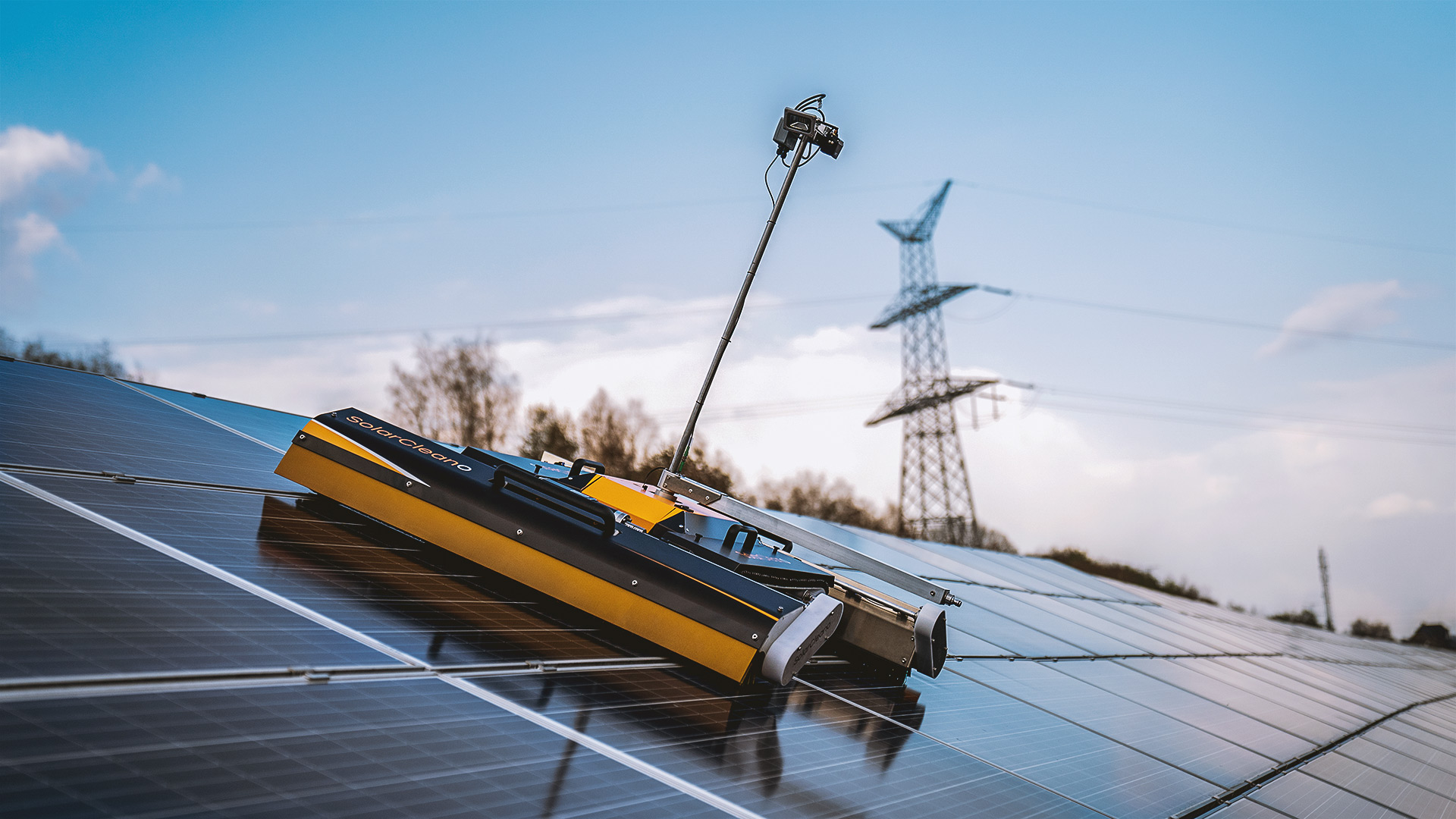
Robot – A semi or fully automated cleaning system which may be used with or without water.
Roofmount – A solar array of any size that is mounted on a roof. Often clarified with the term ‘residential’ or ‘commercial’.
Rotary Brush – An electric or fuel-driven brush that is mounted on a telescopic pole and spins either horizontally or vertically to clean solar panels. WARNING! Danger to life due to electric shock. Rotary brush poles have differing degrees of carbon in them at manufacture stage and are electricity conductors. Use only with correct P.P.E. when cleaning solar panels.
S
Scaling – The process of mineral build-up on the surface of a solar module, often caused by using impure or tap water for solar panel cleaning.
Single Axis Tracker – These solar arrays tilt on one axis, tracking the sun from east to west during the day.
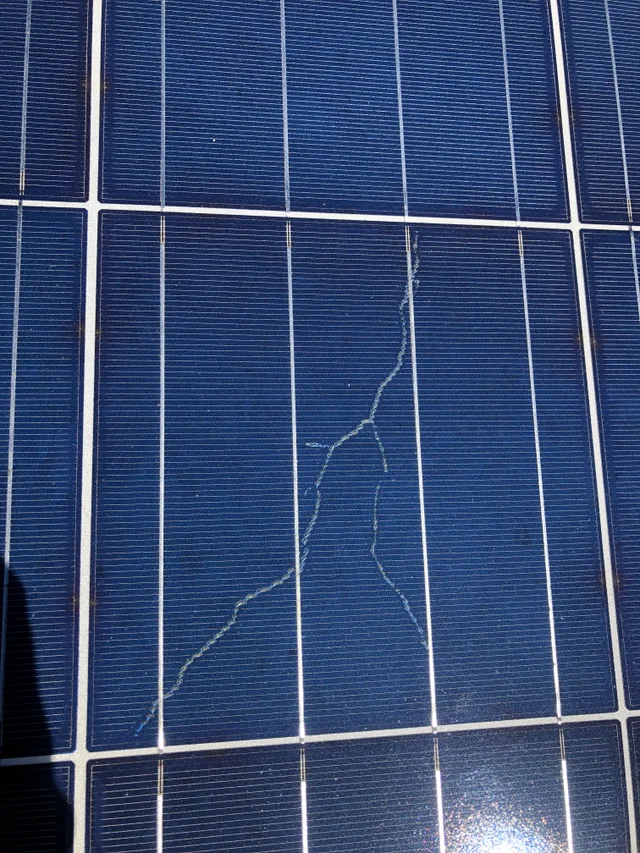
Snail Trail – Lines of local discoloration that occur on solar panels after long-term usage. Snail Trails cause resistance to the flow of current in solar panels, which results in hotspots and a reduction in solar panel efficiency.

Soft shading – A shadow cast on to a solar panel that is always on the move, such as a tree branch blowing in the wind, chimney or shadow from a person working on an array.
Solar Array – A collection of two or more solar modules.
Solar Carport – A solar array that doubles up as a canopy to keep cars sheltered.
Solar Cell – A semi-conducting material that converts light to DC electricity. It is the smallest generating element of a solar system.
Solar Energy – Thermal energy or electricity created from the sun’s radiation.
Solar Farm/Park – A site where a ground mounted solar system is located.
Solar Installation/System – The whole fabric of the many electricity creating and converting components, including the panels, cabling, inverter and other components.
Solar Panel – A collection of solar cells that convert the sun’s energy into electricity.
Solar Power – Energy harnessed from the sun’s light.
String – A group of panels that are wired into a single input on your inverter.
T
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) Meter – A small hand-held device used to indicate the Total Dissolved Solids in a solution, usually water. Since dissolved ionized solids, such as salts and minerals, increase the conductivity of a solution, a TDS meter measures the conductivity of the solution and estimates the TDS from that reading.
Terawatt – 1,000 Gigawatts
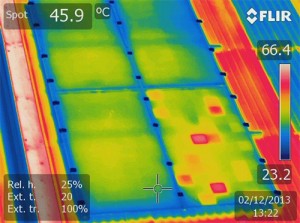
Thermal Imaging – An infrared camera produces thermal images. These help to visualise defects on new and existing solar installations. It is an efficient method for detection of power losses and a wide range of local faults and irregularities.
U
Utility-Scale – A common term that used to solely describe ground mounted solar arrays >1MW in size. However, this term is also now being used to describe multi-MW roof mounted solar arrays also.
V
Visual Inspection – A hands-off inspection of the whole solar array for signs of damage, slippage, wear and tear or other fault or malfunction.
Voltage – This is the system power divided by the system current. An analogy is the pressure in a water pipe.
Voltage Drop – The loss of voltage (electrical pressure) cause by resistance in wire and electrical devices. An analogy is the friction loss in a water pipe.
W
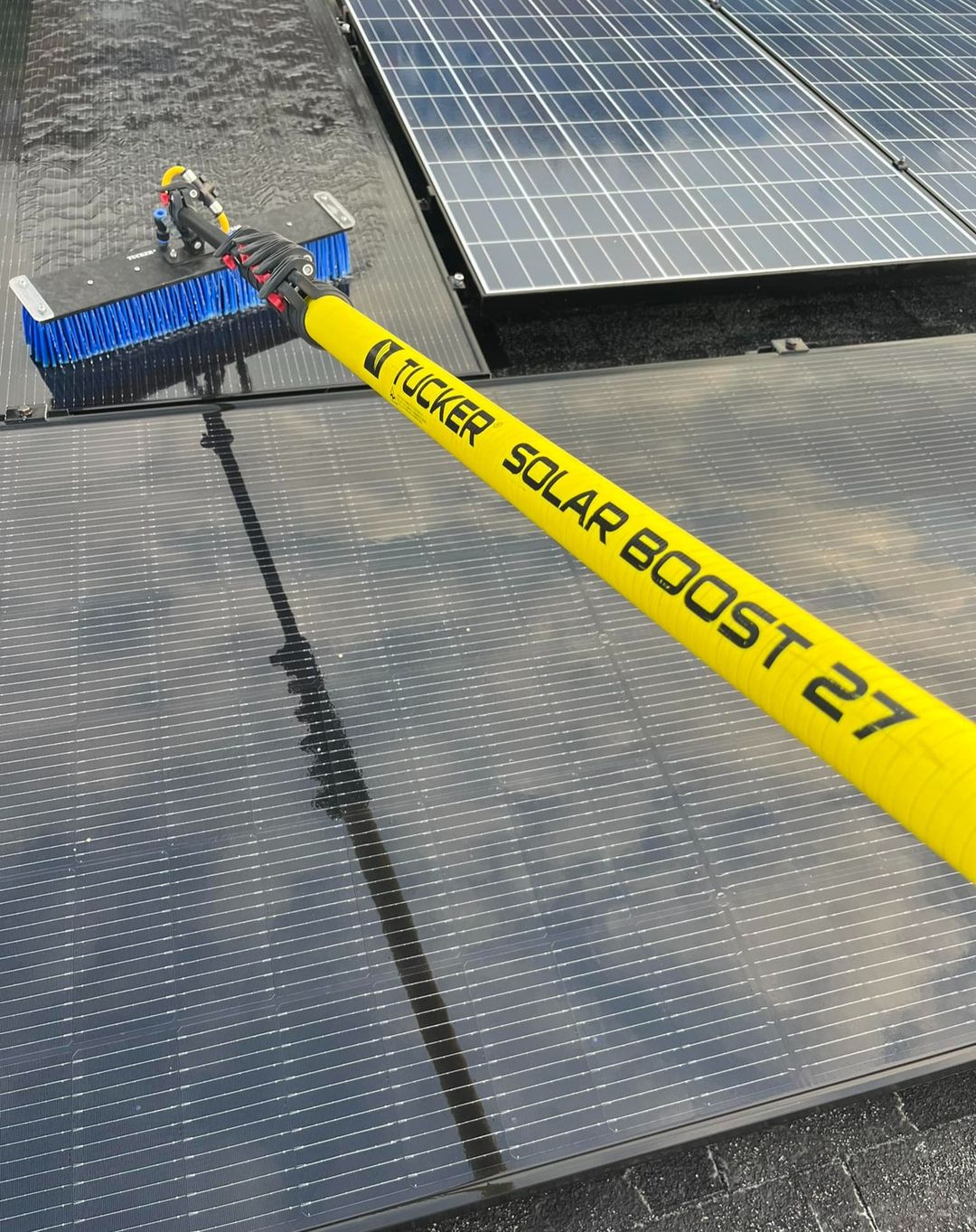
Water-fed Pole (WFP) – A long extendable pole with a brush head. WARNING! Danger to life due to electric shock. Water-fed poles have differing degrees of carbon in them at manufacture stage and are electricity conductors. Use only with correct P.P.E. when cleaning solar panels with any water-fed pole. Below is an example of an ideal water-fed pole for solar panel cleaning.
Watts – Measures total electrical power.
Wp – The peak power that a solar cell/module can produce.
We hope you find this glossary useful and informative!





Leave A Comment